DAF XF 250M, XF 280M, XF 315M, XF 355M Engine Workshop Manual
DAF XF 250 M, XF 280 M, XF 315 M, XF 355 M Engine
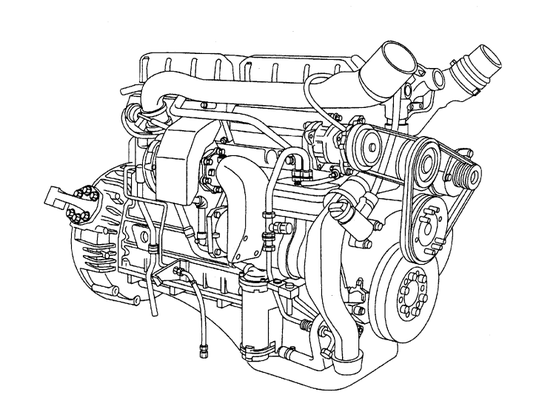
The DAF XF engine repair manual contains detailed instructions on maintenance, diagnostics, and repair of all major engine systems. It covers the fuel, cooling, and lubrication systems, valve adjustment, and assembly and disassembly of the cylinder block, head, and attachments. This document will help service technicians and DAF XF truck owners accurately perform repairs and maintenance according to factory standards.
XF Engine Full Workshop Manual
| Password for PDF: truckfixdiagn.com | |
| XF Engine Technical data | Download |
| XF Engine Diagnosis | Download |
| XF Engine Construction parts | Download |
| XF Engine Fuel system | Download |
| XF Engine Cooling system | Download |
| XF Engine Timing gear | Download |
| XF Engine Flywheel and flywheel housing | Download |
| XF Engine Cylinder head. Removal and Installation | Download |
| XF Engine Lubrication system | Download |
| XF Engine Cylinder block and driving gear | Download |
Typical problems with the XF M series of engines
⚙️ 1. Fuel Injection System
Worn fuel injection pumps and injectors lead to unstable operation, smoking, and loss of power.
Air leaks in the fuel lines lead to difficult starting, especially when cold.
Contaminated fuel often causes accelerated plunger wear.
Solution: Regularly clean and inspect injectors every 150,000–200,000 km, and replace filters as scheduled.
🌡️ 2. Engine Overheating
Faulty fan clutch or thermostat.
Clogged radiator or faulty water pump.
Overheating often damages the cylinder head gasket.
Solution: Monitor the cooling system and flush the radiator every 50,000–70,000 km.
🔩 3. Oil Leaks
Weak points include the valve cover gaskets, oil pan, and front crankshaft oil seal.
Leaks may occur from the turbocharger and oil line connections.
Solution: Use original gaskets and check the crankcase ventilation.
🌀 4. Turbocharging
Turbine bearing wear and axial play.
Decreased boost pressure → loss of power and increased fuel consumption.
Often associated with unscheduled oil changes.
Solution: Change the oil every 25,000–30,000 km, check the boost pressure and ensure the air intake is clean.
🧯 5. Lubrication System
Loss of oil pressure due to wear of the oil pump.
Poor quality oil may cause crankshaft bearing wear.
Solution: Use recommended oils (15W-40 CI-4 or equivalent), change filters.
🧱 6. Mechanical
Worn cylinder liners, especially when overheated.
Loose cylinder head bolts → coolant and compression leaks.
In older engines, cracks in the cylinder head between the valves are common.
Solution: Check compression, tighten the cylinder head torque, and promptly repair at the first sign of trouble.
🔌 7. Electrical and Sensors
Faulty oil temperature and pressure sensors.
Damaged wiring near the fuel rail.
Solution: Regular diagnostics, checking contacts and connectors.
All content on TruckFixDiagn.com is taken from free sources and is also freely distributed. We do not sell repair manuals. Our goal is to help you find all available technical documentation in one place.
The site administration does not bear any responsibility for illegal actions, as well as any damage incurred by copyright holders.